Deploying on GitHub Pages
GitHub offers free hosting for static websites through its GitHub Pages feature. It also has builtin support for Jekyll website. Once properly configured, every time you push your Jekyll website to GitHub, it will be deployed on a username.github.io/reponame url.
But GitHub will only build your website (jekyll build), it will not run other commands (like jekyll algolia), so if you want to update your search results on each push, you’ll have to find another way. This can be done using GitHub Actions, or via a Continuous Integration provider like Travis CI.
We recommend using Netlify to host the whole pipeline, but if you want to stay hosted on GitHub pages, this page will explain how to keep your search records in sync with your deployed website.
Using GitHub Actions
First enable GitHub Actions on your account, and then create this new action under for example .github/workflows/algolia-search.yml.
on push branches master main namealgolia-search jobs algolia-search runs-onubuntu-latest steps usesactions/checkout@v2 usesactions/setup-ruby@v1 with ruby-version'2.6' usesactions/cache@v2 with pathvendor/bundle key$ runner.os -gems-$ hashFiles('**/Gemfile.lock') restore-keys ${{ runner.os }}-gems- nameBundle install run bundle config path vendor/bundle bundle install --jobs 4 --retry 3 nameExec jekyll algolia runbundle exec jekyll algolia env ALGOLIA_API_KEY$ secrets.ALGOLIA_API_KEY
Then create ALGOLIA_API_KEY secret in the repository settings > secrets with the Admin API Key.
Using Travis CI
Enabling Travis
Travis CI is an hosted continuous integration service, and it’s free for open-source projects. It can listen to any changes in your GitHub repository and run a specific command in response.
We will use it to automatically run jekyll algolia every time a new push to
your GitHub Pages is done.
Here are the steps to follow to setup your Travis account for your project:
- Go to travis-ci.org and open an account
- Click on your avatar and “Profile”
- Find your GitHub repository in the list and activate it
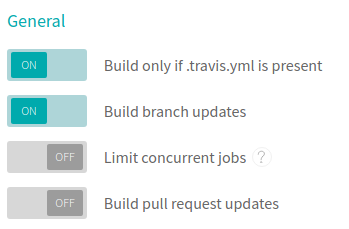
You should also uncheck the “Build pull request updates” in the options. This will avoid re-indexing your data every time you receive a pull request.
Configuring Travis
Now that Travis is enabled, we have to configure it to tell it what to do on
every new push to your repo. This can be done through the Travis UI, but we
recommend doing it through a .travis.yml file in your repository. It makes
keeping track of the configuration easier.
# .travis.yml # This file should be at the root of your project languageruby cachebundler before_install gem install bundler script bundle exec jekyll algolia branches only # Change this to gh-pages if you're deploying using the gh-pages branch master rvm 2.4
This file will be read by Travis and instruct it to fetch all the dependencies
defined in the Gemfile through Bundler. It will then run bundle exec jekyll algolia which will actually index your data.
You might have to edit the branches.only value to either master or
gh-pages, depending on which branch is configured to be deployed in your
GitHub Pages configuration.
Ignoring vendors
Travis bundles all gems in the vendor directory on its servers, which Jekyll
will mistakenly read. This will likely make the process fail. To avoid this,
add vendor to the exclude list in your _config.yml file.
excludevendor
Adding the API Key
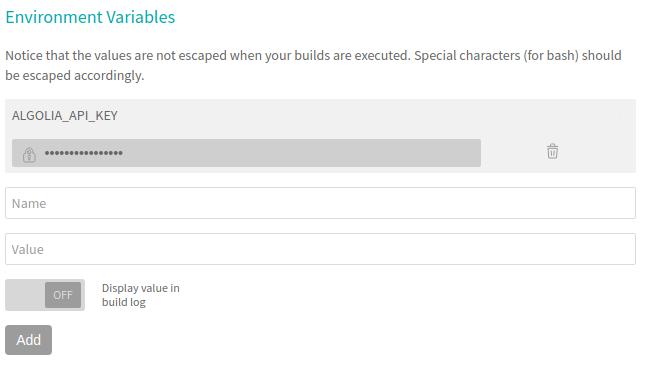
The plugin will need your Admin API key to push data. Because you don’t want to
expose this key in your repository, you’ll have to add ALGOLIA_API_KEY as an
environment variable to Travis. You can do that through the UI, in your Travis
Settings page.
Done
Commit all the changes you made, and then push your repository. Travis will catch the event and trigger your indexing for you. You can follow the Travis job execution directly on your Travis dashboard, with a full log.